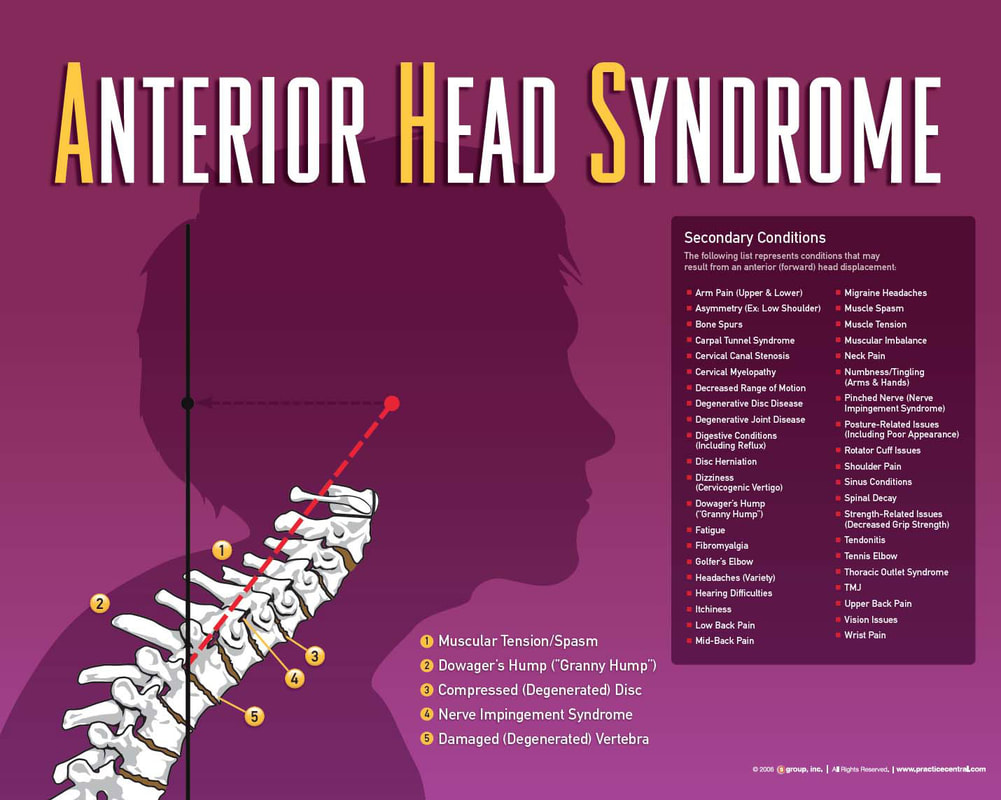
Once a Neural Abnormality is present and disrupting the spinal nerves and spinal cord, it can create many different secondary conditions or symptoms. The reason these are called secondary conditions is because they are a result of the primary Neural Abnormality, or the underlying cause. The location of the Neural Abnormality and where the nerves are being disrupted will give us an idea about your secondary conditions. Some of these include:
- Acid Reflux
- Allergies
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Anxiety
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Attention Deficit Disorders
- Autoimmune Conditions
- Auditory (ear) dysfunction
- Bell’s Palsy
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Chronic Pain
- Colic
- Depression
- Digestive Disorders
- Disc Bulges or Herniations
- Dystonia
- Epilepsy
- Fibromyalgia
- Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
- Headaches
- High Blood Pressure
- Hyperactivity (ADHD)
- Immune Function
- Irritable Bowel syndrome
- Knee Pain
- Learning Disorders (children/adult)
- Lou Gehrig's Disease
- Low Back Pain
- Lyme's Disease
- Menstrual Disorders
- Meniere’s Syndrome
- Mental Illness
- Migraine Headaches
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis
- Neck Pain
- Neurologic Dysfunction
- Otitis Media (Ear infections)
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Shoulder and arm pain
- Seizure Disorders
- Skin Disorders
- Sports Injuries
- Stress
- TMJ Disorder/Dysfunction
- Torticollis
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Ulcers
- Upper Cervical Pain
- Vertigo / Dizziness
- Visual / Eye Disturbances
- Whiplash
- ZZZ ~ Sleep Disorder